The above image is just an animated gif file. Click the above button or this link to launch this interactive activity.
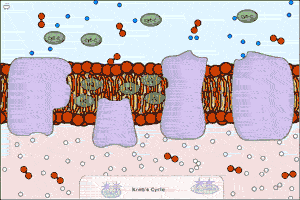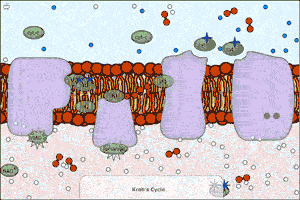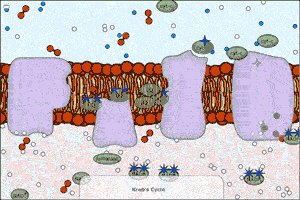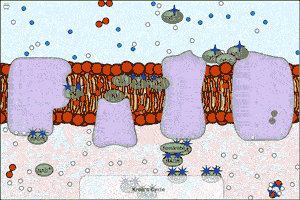
| An electron transport chain couples a chemical reaction between an electron donor (such as NADH) and an electron acceptor (such as oxygen molecules) to the transfer of protons across a membrane, through a set of mediating biochemical reactions. These protons are used to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy intermediate in living organisms, as they move back across the membrane. Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy from sunlight in photosynthesis and from redox reactions such as the burning of sugars in respiration. The following simulation shows this complex process. Note that this is a raw model (we are working on making it more educationally useful). The polygons represent electrons in different excited states. |

The above image is just an animated gif file. Click the above button or this link to launch this interactive activity. |
| System requirements: You must have Java Version 5 or higher in order to run this program. Please go to java.com to get the latest Java software, if you are not sure. |
| Failed? Check out the FAQ for troubleshooting. |